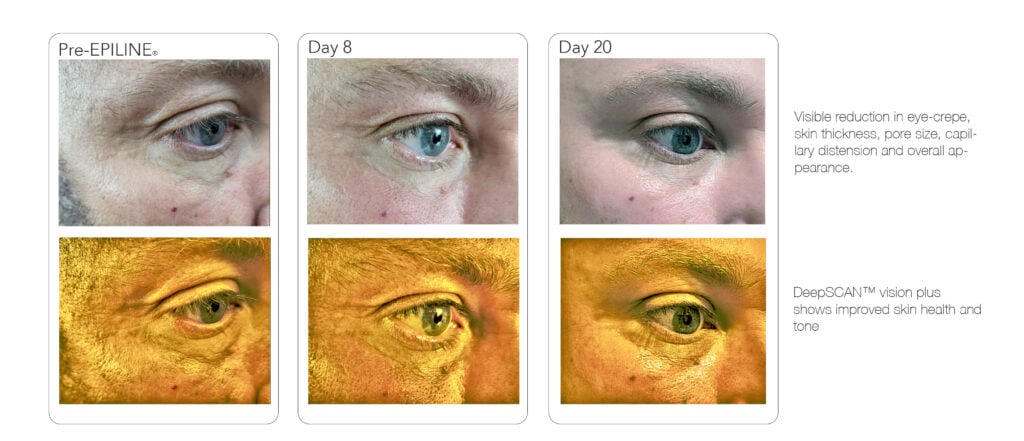
The Science Behind Geneworks
Reliable, proven results.
Use your body’s own DNA expression to regenerate skin cells, repair surface damage, and regain firmness and elasticity.
Bioactive Proteins
Geneworks uses identically-replicated, carefully preserved bioactive proteins that prompt new skin cell generation.
Specialized Delivery System
Our freeze-dried, bioactive proteins attach to cell-penetrating peptides that move beyond the skin’s surface where new skin cells are produced
Bio-synthesized in the Geneworks laboratory.Bio-synthesized in the Geneworks laboratory.
Geneworks uses laboratory replicated, genetically engineered cells as the base for our global patent-pending blend of 9 Umbilical-Cord Human Growth Factor Proteins, uniquely harvested and packaged to maintain bioactivity during manufacturing and delivery. Our identically replicated proteins regulate skin growth to:

Gentle Manufacturing
Geneworks scientists engineered replicated umbilical cord stem proteins that naturally deliver DNA instruction to skin cells.
Freeze Dried
Geneworks genetically engineered proteins are cryo-genomically freeze-dried to preserve optimal freshness and ensure bioactive proteins with every Epiline application.
Protein Delivery Method
Cell Penetrating Peptides

Penetrate The Protective Layers of the Skin
Delivering bioactive growth factors is only the first step in the science of successful skin care. Geneworks attach our proteins to cell-penetrating peptide sequences that open up space in and pass through the skin’s protective layers.
Deliver to cells and immediately accept signal
Once absorbed by the skin’s receptor cells, Geneworks’ bioactive stem cell proteins get to work, delivering DNA-derived instructions to skin cells to reverse signs of aging, repair damage, and restore vibrant color and texture.
Delivering 9 Broad Spectrum Growth Factor Proteins
The Epiline Blend
As pioneers in skincare, Epiline scientists deliver a unique product formulation that harnesses the power of nine broad spectrum growth factor proteins.
EGF
Epidermal Growth Factor
EGF is a member of the EGF-family of proteins, which also includes TGFα and amphiregulin. EGF exerts its effects by binding to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). It is a potent mitogen that stimulates cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation in various cell types, particularly epithelial cells. It also plays a significant role in wound healing, angiogenesis, and tissue remodeling.
bFGF
Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor
Also known as FGF-2, bFGF is a member of the Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family. It binds to FGF receptors (FGFRs) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans, triggering intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, proliferation, migration, and differentiation. bFGF is essential in angiogenesis, wound healing, and tissue repair. It also maintains the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells and induces the formation of new neurons in the adult brain.
VEGF
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
VEGF is a member of the VEGF family of growth factors that includes VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D, and placental growth factor (PlGF). VEGF-A is the most well-known isoform and plays a crucial role in angiogenesis. It binds to VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) on endothelial cells, stimulating their proliferation, migration, and survival. VEGF is essential in the growth of new blood vessels during development, tissue repair, and tumor formation.
PDGF-AA
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-AA
PDGF-AA is one of the five isoforms of the PDGF family, which also includes PDGF-BB, -AB, -CC, and -DD. PDGFs exert their effects by binding to PDGF receptors (PDGFRs) and activating intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, proliferation, and migration. PDGF-AA primarily targets mesenchymal cells, such as fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells, and is involved in the formation of blood vessels, wound healing, and tissue repair.
TGFβ
Transforming Growth Factor-beta
TGFβ is a member of the TGFβ superfamily, which also includes Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) and Growth Differentiation Factors (GDFs). TGFβ signals through TGFβ receptors and downstream SMAD proteins, modulating cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix production. It plays a critical role in tissue homeostasis, wound healing, immune regulation, and fibrosis. Dysregulation of TGFβ signaling is implicated in various diseases, including cancer and fibrotic disorders.
KGF
Keratinocyte Growth Factor
Also known as FGF-7, KGF is a member of the Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family. KGF specifically targets keratinocytes, the primary cell type found in the epidermis. It binds to the FGFR2b receptor, promoting keratinocyte migration, proliferation, and differentiation. KGF plays a vital role in skin homeostasis, wound healing, and barrier function.
GDF-11
Growth Differentiation Factor 11
GDF-11, also known as BMP-11, is a member of the TGF-β superfamily and is closely related to GDF-8 (myostatin). GDF-11 is synthesized as a precursor protein that undergoes proteolytic cleavage to generate the mature, biologically active form. GDF-11 signals through activin type II receptors (ActRIIA and ActRIIB) and ALK4 or ALK5 type I receptors, leading to the activation of downstream SMAD2/3 transcription factors. GDF-11 has been implicated in the regulation of various biological processes, including cell differentiation, tissue homeostasis, and regeneration. Studies have suggested that GDF-11 levels decrease with age, and its administration in aged mice has been shown to rejuvenate multiple tissues, including the heart and skeletal muscle. However, the precise role of GDF-11 in aging and tissue regeneration remains an area of active investigation.
IGF-1
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
IGF-1 is a peptide hormone that shares structural homology with insulin and is part of the IGF family, which also includes IGF-2 and several IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs). IGF-1 is predominantly synthesized in the liver in response to growth hormone (GH) stimulation, although it can also be produced locally by various tissues. IGF-1 exerts its effects by binding to the IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R), a tyrosine kinase receptor that activates multiple intracellular signaling pathways, including the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. These pathways regulate cell growth, differentiation, survival, and metabolism. IGF-1 plays a vital role in growth and development, particularly during childhood and adolescence, and is essential for maintaining bone density, muscle mass, and metabolic homeostasis. Dysregulation of IGF-1 signaling has been implicated in several diseases, including cancer, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
HGF
Hepatocyte Growth Factor
HGF, also known as Scatter Factor (SF), is a pleiotropic growth factor that targets various cell types, particularly hepatocytes. HGF binds to the MET receptor, activating intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, survival, migration, and morphogenesis.